
In today’s evolving world, energy efficiency, security, and sustainability demand is at an all-time high. Traditional energy management systems are proving insufficient due to rising energy demands, unpredictable renewable sources, and potential cybersecurity threats. This is where integrating Blockchain with AI for smart grid management comes into play. The convergence of these two groundbreaking technologies promises to revolutionise how we manage energy and ensure that our energy systems are more secure, transparent, and efficient than ever before. Through intelligent automation and decentralized operations, Blockchain and AI are set to pave the way for a new era of smart grid management.
Blockchain and AI: A Game-Changer for Energy Management
Blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) convergence is reshaping the energy sector. These technologies offer transformative solutions to some of the industry’s most pressing challenges, driving efficiency, security, and sustainability. The Global AI in Energy Market size is expected to be worth around USD 51.4 Billion by 2033, from USD 3.7 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 30.1% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
Key Benefits of Blockchain and AI in Energy Management
Boosting Energy Efficiency
- AI-Driven Optimization: AI analyzes vast energy consumption data to identify inefficiencies and optimize usage, minimizing waste.
- Blockchain-Powered Smart Grids: Blockchain enables decentralized grids integrating renewable energy sources, enhancing distribution efficiency and system reliability.
Enhancing Grid Reliability
- Real-Time Tracking: Blockchain provides a secure, transparent ledger for real-time energy monitoring, reducing fraud and errors.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI predicts equipment failures, ensuring timely maintenance and minimizing downtime, strengthening grid reliability.
Strengthening Energy Security
- Immutable Data: Blockchain’s tamper-proof records safeguard energy transactions from cyber threats and fraud.
- Decentralized Energy Markets: Blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading, reducing reliance on centralized grids and improving system resilience.
Accelerating Renewable Energy Adoption
- Peer-to-Peer Trading: Blockchain enables consumers to directly buy and sell renewable energy, promoting decentralized energy markets.
- Transparent Energy Certificates: Blockchain ensures verifiable renewable energy generation, fostering trust and transparency.
Transformative Use Cases
- Smart Grids: Combining AI and Blockchain can optimize energy flow and improve grid stability, reducing waste and enhancing efficiency.
- Decentralized Trading: Blockchain supports peer-to-peer energy markets, while AI forecasts demand and supply trends for seamless transactions.
- Energy Efficiency: AI optimizes energy use in homes and businesses, with Blockchain ensuring transparent and accountable management.
- Grid Modernization: Blockchain enables the integration of electric vehicles and battery storage, enhancing grid flexibility.
AI in Smart Grid Management: Revolutionizing Energy Distribution
AI transforms smart grid management, making energy systems more efficient, reliable, and sustainable. By leveraging AI, grids can optimize operations, reduce downtime, and better integrate renewable energy sources.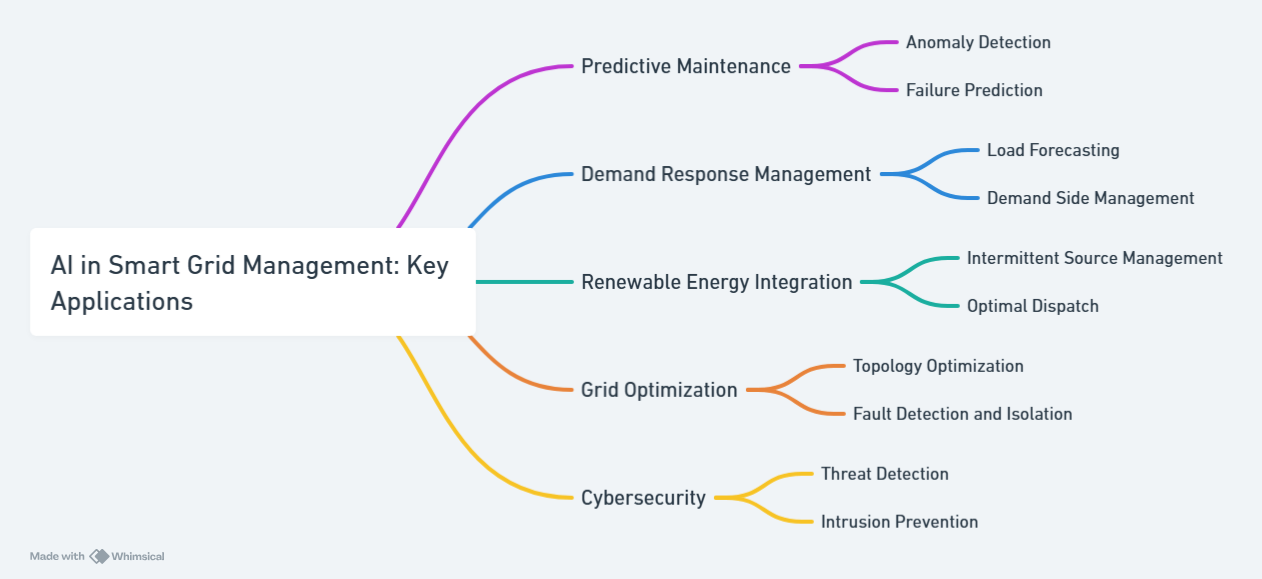
Critical Applications of AI in Smart Grids
Predictive Maintenance: AI monitors grid components in real-time, predicting failures and scheduling preventive maintenance to minimize downtime and repair costs.Demand Response Optimization forecasts electricity demand, adjusts energy use during peak periods, and encourages consumers to reduce load, ensuring grid stability.Renewable Energy Integration: It also manages the intermittent nature of renewable sources like solar and wind, balancing supply and demand for a stable grid.Energy Efficiency Optimization: AI analyzes smart meter data to identify energy-saving opportunities and recommends efficiency measures to consumers.Fraud Detection & Cybersecurity: AI detects anomalies in energy usage to prevent fraud and enhances grid security, protecting against cyberattacks.
Decentralization: A Key Factor in Smart Grids
Decentralization is vital to smart grids, offering enhanced reliability, security, efficiency, and flexibility. Decentralized systems reduce vulnerability to disruptions like natural disasters or cyberattacks by distributing power generation and control across multiple nodes. They enable localized power generation through distributed energy resources (DERs) such as solar and wind while improving grid efficiency by optimizing power flow based on local demand. Decentralization also empowers consumers to generate and trade energy, promoting a more sustainable and equitable system. Despite challenges like interoperability and grid stability, the benefits of decentralization make it a key foundation for a resilient, modern energy infrastructure.
Energy Security: Tackling Cyber Threats with Blockchain
One of the primary concerns in smart grid management is cybersecurity. As grids become more connected and reliant on real-time data, they become prime targets for hackers. Blockchain technology offers a robust solution to this challenge. Its decentralized structure ensures that no single entity controls the entire grid, making it significantly harder for cybercriminals to compromise the system.
Specific Use Cases of Blockchain in Energy Security
Grid Management ensures the secure, transparent tracking of energy generation, consumption, and distribution, improving grid integrity and efficiency.Renewable Energy Certificates: This department verifies the authenticity of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs), ensuring they accurately represent renewable energy production.Cybersecurity Threat Detection: This system monitors energy consumption patterns, detecting anomalies that may indicate cybersecurity threats and enabling quicker responses.Energy Trading: It Facilitates secure, transparent energy trading, reducing the risk of fraud and market manipulation.
Data Integrity: Why Blockchain matters in AI-driven grids
Data integrity is crucial for accurate decision-making and optimized grid operations in AI-driven smart grids. Blockchain ensures the data fed into AI models is secure, tamper-proof, and verifiable. Its immutability prevents data alteration, while transparency allows stakeholders to trace and verify data origins. The decentralized structure enhances security, making it difficult to compromise the system. Blockchain’s suitability and trust-building features enable reliable tracking of grid operations, energy trading, and renewable energy certificates. These qualities ensure AI systems operate confidently, improving overall grid efficiency and resilience against cyber threats.
Real-World Examples of AI-Blockchain Integration in Energy Grids
AI and Blockchain are being used together to improve energy grid efficiency, security, and transparency:
New York City DOT
- Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes sensor data to predict equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance.
- Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading: Blockchain allows consumers to trade energy directly.
Energy Web Foundation (EWF)
- RECs Tracking: Blockchain verifies renewable energy certificates.
- Smart Grid Integration: Blockchain enables secure energy data exchange and new business models.
LO3 Energy
- Local Energy Trading: Blockchain facilitates energy trading within communities.
- AI Optimization: AI enhances grid efficiency by optimizing energy management.
Sunverge Energy
- DERs Management: Blockchain manages solar and battery resources.
- AI-Powered Optimization: AI improves resource efficiency and grid stability.
Power Ledger
- Peer-to-Peer Trading: Blockchain enables direct energy trading among consumers.
- Smart Meter Integration: Accurate transaction settlement via smart meters.
These examples highlight how AI and Blockchain transform energy grids by enhancing automation, transparency, and decentralization.
Technological Innovations Driving Blockchain and AI in Smart Grids
The rapid development of cutting-edge technologies accelerates the integration of Blockchain and AI in smart grids, fostering more sustainable and efficient energy solutions. Below are key advancements supporting this transformation: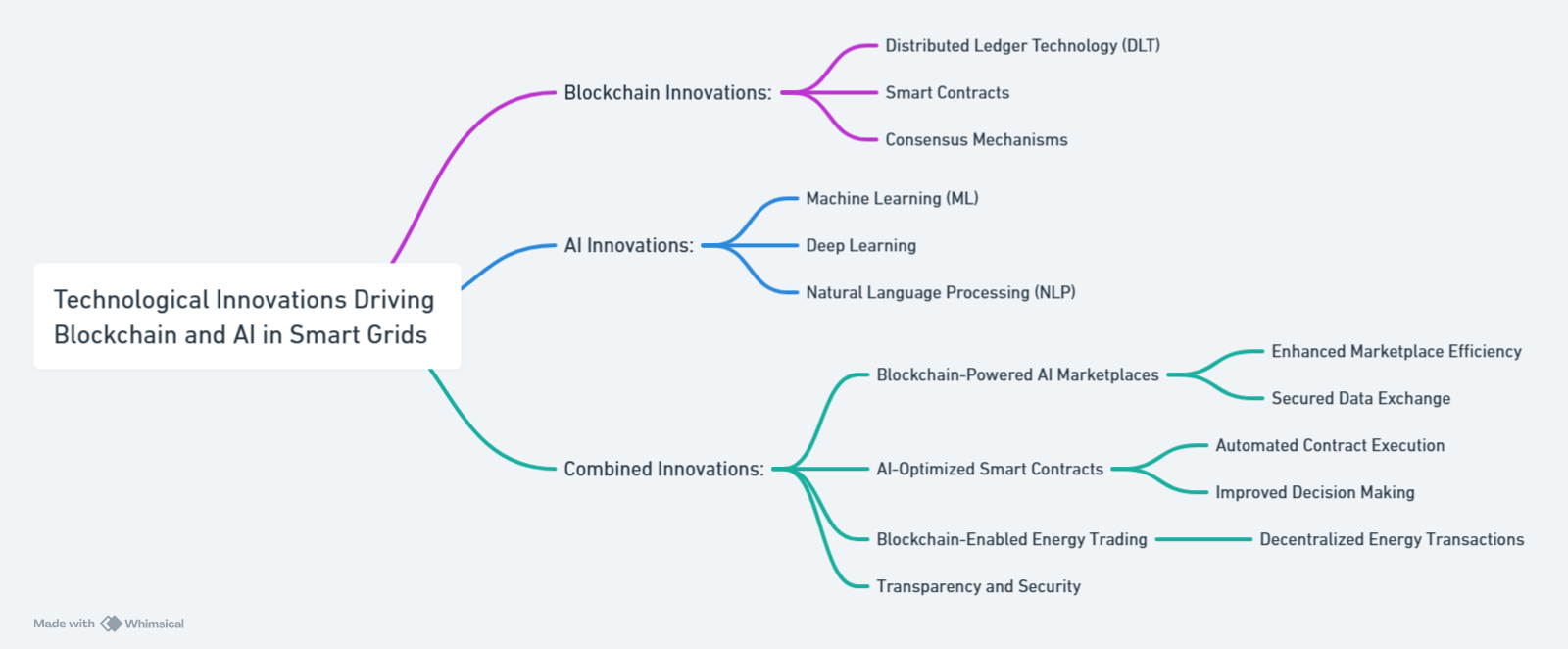
Edge Computing
- Real-Time Processing: Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, enabling real-time analysis and faster decision-making in energy grids.
- Low Latency: By handling data locally, edge computing minimizes latency, which is crucial for responsive, time-sensitive applications in smart grid management.
Internet of Things (IoT)
- Data Generation: IoT devices collect vast amounts of data from energy assets, providing critical input for AI algorithms to optimize grid performance.
- Blockchain Integration: Integrating IoT with Blockchain ensures the security and integrity of the data these devices generate, fostering trust in automated grid systems.
Machine Learning
- Advanced Analytics: Machine learning processes complex energy consumption patterns, enabling AI to make smarter predictions and optimize energy flow.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing equipment health, machine learning can anticipate failures and recommend preventive maintenance, improving grid reliability and lowering costs.
Quantum Computing
- Enhanced Security: Quantum computing offers the potential to create ultra-secure cryptographic systems, safeguarding sensitive energy data from cyber threats.
- Optimization Efficiency: With quantum computing’s ability to solve complex optimization problems faster, smart grids can experience enhanced performance and more efficient energy distribution.
Blockchain Scalability Solutions
- Layer 2 Protocols: Technologies like the Lightning Network and Plasma offer scalability improvements, allowing blockchain systems to handle more transactions per second.
- Sharding: By splitting blockchains into smaller, manageable shards, this technology increases transaction throughput by enabling parallel data processing.
AI-Powered Smart Contracts
- Sophisticated Automation: AI enhances smart contracts by enabling them to adapt to dynamic conditions, improving the automation of energy trading and grid management.
- Predictive Capabilities: AI-driven smart contracts use predictive analytics to anticipate energy demand or other market changes, adjusting terms and optimizing transactions accordingly.
These technological advancements propel the synergy between Blockchain and AI, paving the way for smarter, more resilient, and sustainable energy grids. As innovation continues, we can expect further breakthroughs, bringing new possibilities to energy systems worldwide.
Conclusion
The integration of Blockchain and AI holds immense promise for the future of smart grid management. Blockchain ensures secure, transparent transactions and data integrity, while AI optimizes energy flow and automates decision-making. Together, they create a resilient, efficient, and secure energy grid capable of handling the complexities of modern energy distribution. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy systems, fostering sustainable practices, and enhancing grid reliability.
FAQs
What is Automation in Smart Grids?
Automation in smart grids involves using cutting-edge technologies, such as sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time data analytics, to monitor, control, and optimize the flow of electricity across the grid. These systems enable automatic responses to grid fluctuations, improving efficiency and reliability without manual intervention. Automated smart grids can adjust energy distribution in real time, detect faults, and even self-heal by rerouting power around problem areas, making energy systems more resilient and responsive.
What are the Four Main Benefits of Smart Grids?
Smart grids offer several significant benefits, including improved energy efficiency by optimizing power distribution and minimizing energy losses. They are instrumental in more effectively integrating renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, into the grid. Additionally, smart grids enhance the reliability of energy supply by quickly detecting and addressing issues, thus reducing outages. Finally, they empower consumers by providing real-time data and dynamic pricing, allowing greater control over energy usage and costs.
What are the Applications of AI in Smart Buildings?
AI plays a crucial role in smart buildings by improving energy efficiency. It can intelligently manage heating, cooling, and lighting systems to minimize waste. It also enables predictive maintenance, where potential issues with building systems are identified and addressed before they cause significant problems, leading to cost savings. AI-driven systems can adjust resources based on occupancy levels, ensuring energy is used efficiently. Additionally, AI enhances building security through advanced surveillance systems and automated access control.
What is the Use of AI in Smart Devices?
AI is widely used in smart devices to enhance user experience through personalization and automation. For example, smart devices like thermostats can learn a user’s preferences and adjust settings automatically for optimal comfort and energy savings. AI also automates routine tasks without user intervention, such as turning off lights or locking doors. Many smart devices incorporate voice control features, allowing users to operate hands-free through voice assistants. Moreover, AI’s predictive capabilities enable these devices to anticipate user needs, improving convenience and functionality.


