Decentralized Finance, commonly called DeFi, represents a broad category of financial applications that use blockchain technology to disrupt traditional monetary systems. DeFi enables users to engage in economic activities like lending, borrowing, and trading without relying on mediators such as banks or financial institutions, thanks to its decentralized nature. The foundation of DeFi lies in blockchain, particularly platforms like Ethereum, which offer smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
By eliminating intermediaries, DeFi offers several benefits: reduced transaction fees, greater transparency, and increased accessibility, especially for individuals who are underresourced by traditional financial systems. This makes DeFi a powerful tool in creating open and inclusive financial networks.
Understanding Carbon Credits
Carbon credits are important tools in the global effort to combat climate change. Each carbon credit stand for one metric ton of carbon dioxide (CO2) that has been either removed from the atmosphere or prevented from being emitted.Organizations, governments, and individuals unable to fully mitigate their carbon emissions can purchase these credits to offset their environmental impact, thereby contributing to international climate mitigation efforts.
The Taskforce on Scaling Voluntary Carbon Markets (TSVCM), sponsored by the Institute of International Finance (IIF) with knowledge support from McKinsey, estimates that demand for carbon credits could increase by a factor of 15 or more by 2030 and by a factor of up to 100 by 2050. Overall, the market for carbon credits could be worth upward of $50 billion in 2030.Cap-and-trade systems assign emission limits to countries or companies, leading to the creation of carbon credits. If they discharge less than their allowance, they can sell their excess credits to others who need them. This market-based approach incentivizes emissions reductions and encourages investment in clean technologies. However, traditional carbon credit markets have faced several challenges, including a need for more transparency, high transaction costs, and limited access for more minor participants.
How Blockchain and DeFi are Revolutionizing Carbon Credit Markets
Integrating blockchain technology into carbon credit markets can address many of the problems associated with traditional systems. Blockchain provides an immutable and transparent ledger for all transactions, ensuring that every carbon credit is verifiable, unique, and cannot be double-counted. This technology enhances the credibility of carbon credits and allows stakeholders to trust that they are genuinely contributing to emissions reductions.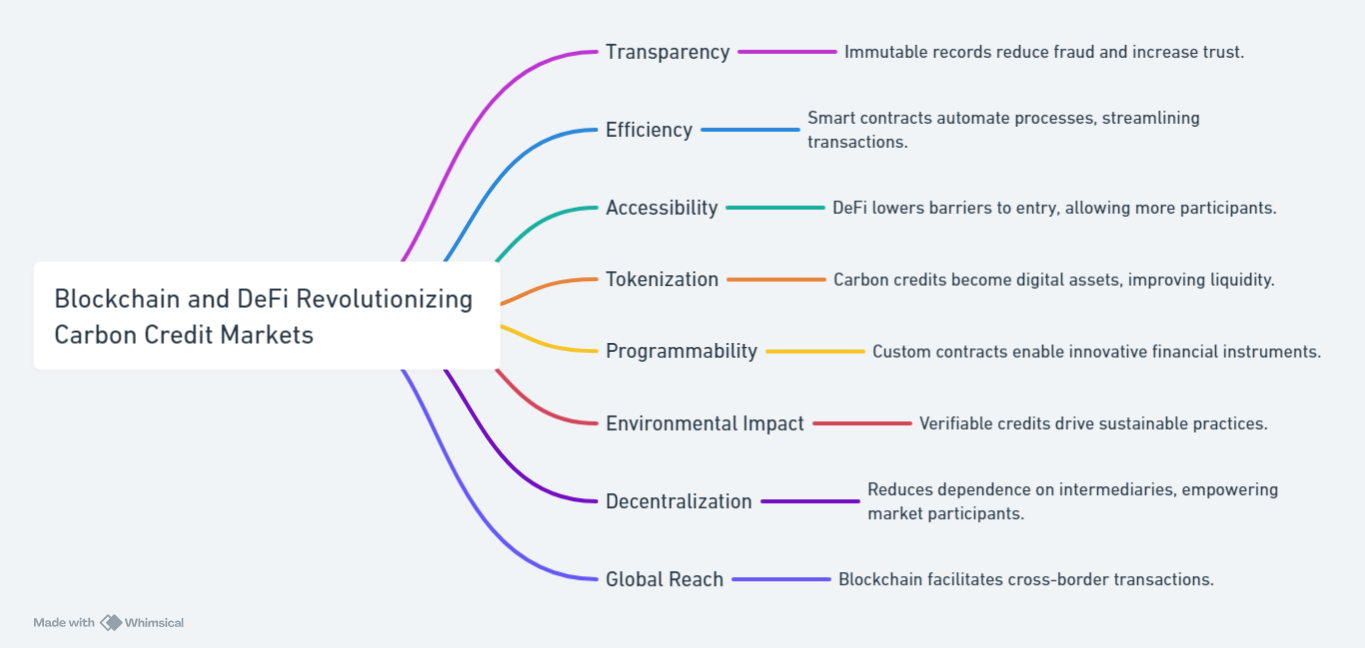 DeFi’s role in this landscape is pivotal, mainly through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automate the trading process, ensuring secure and efficient buying, selling, and retiring of carbon credits. By removing the need for mediators, DeFi platforms reduce transaction costs and increase accessibility, allowing individuals and organizations worldwide to participate in carbon markets.
DeFi’s role in this landscape is pivotal, mainly through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automate the trading process, ensuring secure and efficient buying, selling, and retiring of carbon credits. By removing the need for mediators, DeFi platforms reduce transaction costs and increase accessibility, allowing individuals and organizations worldwide to participate in carbon markets.
Tokenization of Carbon Credits
Tokenization is a key innovation that involves converting carbon credits into digital tokens that can be traded on blockchain platforms. This digital transformation brings numerous benefits:
Liquidity
Tokenized carbon credits can be traded more frequently, leading to increased liquidity in carbon markets. Participants can buy and sell credits quickly, ensuring a more dynamic trading environment.
Fractional Ownership
Tokenization enables the division of carbon credits into smaller fractions, allowing individuals and small businesses to purchase and trade portions of credits. This democratizes access to carbon markets and encourages broader participation.
Global Accessibility
Blockchain technology facilitates cross-border transactions, breaking down geographical barriers that often restrict participation in traditional carbon markets. This opens up opportunities for investors and organizations worldwide to engage in carbon trading.Smart contracts further enhance the efficiency of these transactions by automating various aspects of the trading process. For example, they can ensure that participants transfer credits only when specific conditions are met, thereby creating a trustless environment for secure trading.
Leading DeFi Platforms for Carbon Credits
Several DeFi platforms are at the forefront of integrating blockchain technology with carbon credit trading. These platforms are pioneering innovative approaches to tokenizing and facilitating carbon credit transactions:
- Toucan Protocol: Toucan is one of the leading platforms in the carbon credit space, focusing on tokenizing verified carbon credits. It allows users to buy, sell, or retire these credits seamlessly, enhancing transparency and liquidity in the carbon market. Toucan aims to create a more open and efficient carbon market that anyone can access.
- KlimaDAO: KlimaDAO operates as a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that aims to incentivize purchasing and retiring carbon credits. By using its treasury to raise the price of carbon credits, KlimaDAO encourages investment in carbon reduction projects.
- Moss.Earth: Moss. Earth specializes in tokenizing carbon credits derived from environmental projects, mainly focusing on conservation initiatives in the Amazon rainforest. This platform allows individuals and companies to purchase tokenized credits, thus contributing to preserving vital ecosystems while offsetting their carbon footprints.
- Flowcarbon: Flowcarbon connects environmental projects with decentralized finance markets by tokenizing carbon credits and creating a transparent, scalable solution for trading. Flowcarbon aims to streamline the trading process by utilising blockchain, making it easier for participants to engage in carbon credit transactions.
- Regen Network: Regen Network utilizes blockchain technology to track and verify ecological data, offering tokenized carbon credits from various sustainability projects, including reforestation. This platform emphasizes the importance of environmental health and aims to create a more equitable carbon credit system.
Trading Carbon Credits on DeFi Platforms
DeFi platforms provide various mechanisms for trading and managing carbon credits, enabling participants to engage in carbon markets effectively:
Liquidity Pools
Users can provide liquidity for carbon credits on decentralized exchanges, earning rewards for their contributions. These liquidity pools enable efficient trading of tokenized carbon credits at competitive prices.
Staking and Yield Farming
Many DeFi platforms offer staking and yield farming opportunities, allowing users to earn returns by locking up their tokenized carbon credits in exchange for governance tokens or other rewards. This incentivizes participants to hold their credits and contributes to market stability.
Decentralized Marketplaces
DEXs enable users to trade tokenized carbon credits directly without relying on a centralized intermediary. This fosters a more open trading environment, allowing participants to negotiate prices and terms directly with one another.
Environmental Impact of DeFi Carbon Credits
Despite concerns about energy consumption linked to blockchain technology, DeFi platforms enhance climate action. They make carbon markets more accessible and efficient. By lowering barriers to entry, these platforms encourage greater participation in carbon markets. This, in turn, drives investment into carbon reduction projects worldwide. This democratization of carbon trading may lead to significant emissions reductions and facilitate the transition to a more sustainable economy.Moreover, blockchain’s ability to provide real-time tracking and verification of environmental impacts enhances the credibility of carbon credits. Participants can access detailed data on emissions reductions and project outcomes, thereby increasing trust in carbon markets and encouraging responsible trading practices.
Future of DeFi in Carbon Credits
The future of DeFi in the context of carbon credits appears promising, with potential developments that could further enhance the efficacy of carbon markets:
Integration with Other DeFi Products
As the DeFi ecosystem matures, there may be opportunities to integrate carbon credits with other financial products, such as loans, insurance, and investment vehicles. This could create new avenues for financing sustainability initiatives and drive innovation in carbon markets.
The Role of AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) could be vital in optimizing trading strategies, enhancing data accuracy, and improving sustainability analyses in carbon markets. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to predict market trends, assess project viability, and evaluate the environmental impact of investments.
Future Trends and Predictions
As awareness of climate change continues to increase, DeFi platforms for carbon credits are likely to see greater adoption. This could lead to more sophisticated trading tools, increased regulatory clarity, and the emergence of new business models focused on sustainability.
Conclusion
Decentralized finance platforms are reshaping the landscape of carbon credit trading, making the process more accessible to a global audience. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, these platforms offer innovative solutions to traditional carbon markets’ challenges.Integrating DeFi and carbon credits represents a transformative opportunity to enhance global climate action as the world grapples with climate change. With the potential to democratize access to carbon markets, drive investment in sustainability, and foster greater accountability, DeFi platforms are positioned to play an important role in reducing carbon emissions and promoting a more sustainable future for all.The evolution of this intersection will not only influence the financial landscape but also contribute significantly to the broader efforts to fight climate change, making it an exciting frontier for investors and environmental advocates alike.
FAQs
Who Issues Carbon Credits?
Various entities issue carbon credits, each playing an important role in the carbon market. Regulatory agencies, such as the California Air Resources Board (CARB) and the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), oversee compliance credits in cap-and-trade systems. Independent standards bodies, like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) and Gold Standard, create methodologies to certify emission reductions. Additionally, project developers implementing initiatives to reduce emissions can generate carbon credits, provided their projects pass rigorous verification processes.
How Many Types of Carbon Credits Are There?
Carbon credits are categorized into two types: compliance and voluntary. Compliance credits are part of regulated carbon trading systems, helping entities meet mandated emission reduction targets. Government-authorized programs issue these. In contrast, voluntary credits are generated from projects outside regulatory frameworks, allowing individuals and organizations to offset their emissions voluntarily. They are often certified by independent standards to ensure their legitimacy.
What Are the Top Carbon Credit Companies?
Several prominent companies are integral to the carbon credit market. Verra is known for its Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), certifying voluntary market projects. Gold Standard ensures that carbon projects yield positive environmental and social outcomes. Climate Action Reserve establishes standards for greenhouse gas emission reductions, promoting transparency. Moss.Earth specializes in tokenizing carbon credits, enhancing accessibility for investors. Lastly, Toucan Protocol is a leading DeFi platform that facilitates tokenising and trading carbon credits on blockchain networks.
How to Tokenize Carbon Credits?
Tokenizing carbon credits involves converting verified credits into digital tokens on a blockchain. The process begins with accredited organisations’ verification of projects, ensuring that the claimed emission reductions are valid. Once verified, the corresponding carbon credits are issued. These credits are then transformed into digital tokens using smart contracts defining their characteristics. Trading platforms list the tokenized credits, enabling participants to trade them efficiently. Blockchain technology ensures transparency and traceability, preventing double counting and enhancing trust in the carbon credit market. This process promotes broader participation in carbon offset initiatives, aligning economic activities with environmental sustainability.