
Intellectual property has long been the backbone of creative industries, science, and technology. However, current systems for protecting IP face numerous issues, including piracy, counterfeiting, and infringement. These problems persist due to outdated and geographically fragmented IP laws, lengthy legal processes, and the challenges of policing digital content worldwide. Such issues have highlighted the need for innovative, adaptable solutions—ones that blockchain marketplaces can provide.
Blockchain-powered intellectual property marketplaces are emerging as secure, transparent platforms for managing IP assets. These marketplaces provide a decentralized solution to traditional IP management challenges, from counterfeiting to complex licensing processes. In a world where digital content is growing exponentially, blockchain marketplaces are paving the way for a new era in intellectual property rights (IPR).
How Blockchain is Transforming IP Marketplaces
Blockchain-powered intellectual property marketplaces leverage the security and transparency of blockchain to create trusted platforms for IP assets. These marketplaces offer a range of services, from registering IP rights to tracking usage and royalties. Blockchain’s transparency allows creators and buyers to trace the origin of IP assets, verify ownership, and engage in secure transactions. By embedding trust and efficiency into IP transactions, blockchain enhances how creators monetize and protect their work globally.
Advantages of Blockchain in IP Management
Blockchain technology offers significant advantages for managing intellectual property (IP) by enhancing security, improving efficiency, and providing new opportunities for revenue generation. Here’s how blockchain can transform IP management: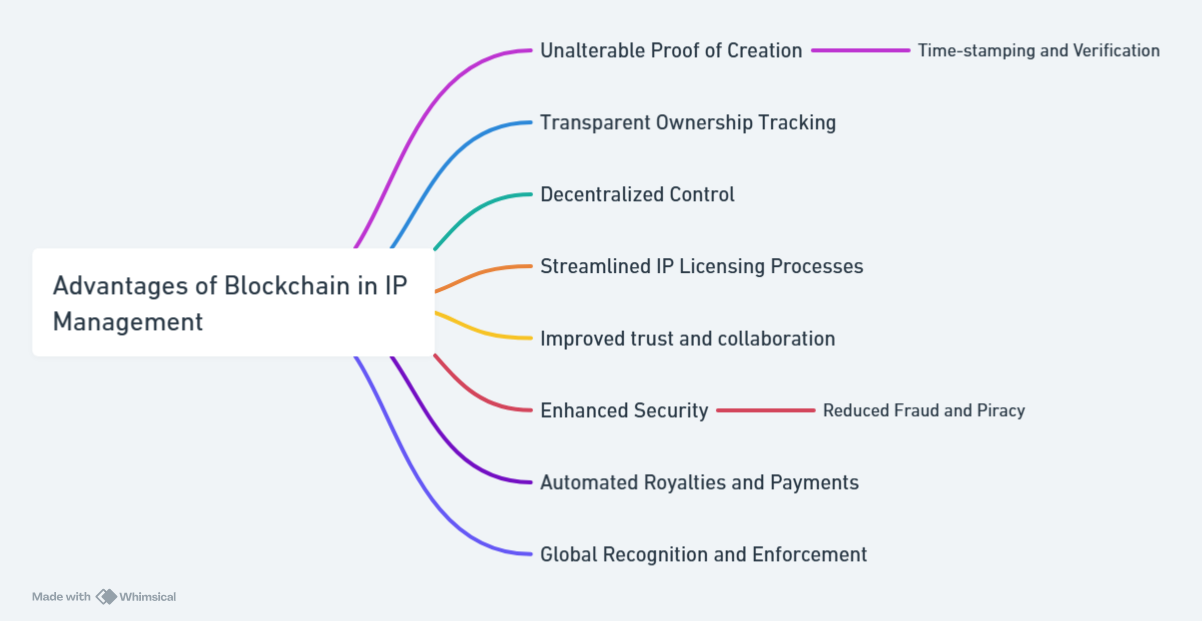
Stronger IP Protection
Blockchain-based IP registries offer global recognition of IP rights, reducing the likelihood of infringement. Furthermore, smart contracts can automate IP licensing and dispute resolution, making these processes more efficient and cost-effective.
Streamlined IP Management
Blockchain can automate time-consuming administrative tasks like IP registration, licensing, and royalty distribution, reducing overhead and increasing operational efficiency. Real-time monitoring of IP assets also allows for greater visibility into their use and value, improving decision-making and control.
Increased Transparency and Trust
With blockchain, ownership records are clear and verifiable, minimizing disputes and legal challenges. A blockchain-powered IP ecosystem fosters greater trust and collaboration among owners, licensees, and other stakeholders by ensuring that all transactions and ownership transfers are transparent and verifiable.
New Revenue Opportunities
Blockchain opens up innovative ways to monetize IP. Tokenization digitizes IP assets and enables their trade on blockchain-based platforms, unlocking new investment and revenue opportunities. Additionally, smart contracts can automate royalty payments, ensuring that creators and stakeholders receive timely and accurate compensation.
Tokenization of Intellectual Property Assets
Tokenization involves converting ownership rights of an IP asset into a digital token on the blockchain. People can buy, sell, or license these tokens, increasing the liquidity and tradability of IP assets. For instance, creators could tokenize a song, patent, or artwork, allowing them to sell portions of their IP or earn royalties each time the token is transferred. This shift to tokenization revolutionizes IP by transforming it into a dynamic, tradable asset within the digital economy.
How Does It Work?
Asset Valuation: The IP asset is evaluated to determine its value and potential market. Tokenization: The asset is divided into smaller, fractionalized units, each represented by a unique digital token. Blockchain Integration: These tokens are minted and recorded on a blockchain, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability. Trading and Exchange: The tokens can be traded on decentralized exchanges, allowing for a global market for IP assets.
Smart Contracts in IP Transactions
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts coded onto the blockchain, enabling automatic transactions based on predefined conditions. In IP marketplaces, smart contracts can be used to automate licensing agreements, royalty payments, and usage tracking. For instance, an artist could establish a smart contract that releases royalties every time a song is streamed, ensuring timely payments and eliminating intermediaries.
Use Cases of Smart Contracts in IP Management
Smart contracts enhance the management of intellectual property (IP) by automating processes and ensuring security. Here are key use cases:
- Licensing Agreements: Automate the issuance, transfer, and termination of licenses, reducing administrative effort and ensuring compliance.
- Royalty Payments: Ensure timely and accurate royalty payments based on usage data, eliminating delays and errors.
- Copyright Protection: Timestamp and secure digital assets on the blockchain to verify ownership and protect copyrights.
- NFT Creation and Trading: Facilitate the creation and trade of NFTs representing unique IP assets, ensuring verifiable ownership and secure transactions.
- IP Asset Management: Track ownership, usage, and value of IP assets in real-time, optimizing management throughout their lifecycle.
Smart contracts improve efficiency, transparency, and security, transforming how IP is handled.
The Role of NFTs in Intellectual Property
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have become instrumental in safeguarding, verifying ownership, and monetizing intellectual property (IP) in today’s digital landscape. By harnessing the capabilities of blockchain technology, NFTs offer innovative solutions to the complexities associated with digital assets and IP rights.
IP Protection and Ownership Verification
- Immutable Record: Minting an NFT on a blockchain generates a permanent, unalterable record of ownership. This feature minimizes disputes and protects the rights of the original creator or current owner.
- Unique Digital Identifiers: Each NFT possesses a distinct digital signature, allowing for easy identification and tracing of ownership history for any digital asset.
- Timestamping: The blockchain captures the exact time an NFT is created, serving as verifiable proof of its origin.
Monetization of Intellectual Property
- Direct Sales: Creators can directly sell their digital works to buyers, eliminating traditional intermediaries and enhancing their revenue potential.
- Automatic Royalties: Smart contracts embedded in NFTs automatically manage royalty distributions, ensuring creators receive a portion of any future sales.
- Fractional Ownership: Splitting NFTs into smaller shares allows multiple individuals to invest in and own portions of a high-value digital asset.
- Licensing Opportunities: NFTs can facilitate the licensing of IP for diverse applications, including merchandise, video games, and other digital products.
Adoption Trends for Blockchain IP Marketplaces
Global Adoption Patterns
The adoption of blockchain technology in IP marketplaces is still emerging but gaining traction. Early adopters include tech-savvy individuals, artists, and creative professionals who recognize the benefits of blockchain for managing intellectual property.Key Regions Driving Adoption:
- United States: A major center for innovation and IP-focused industries.
- Europe: Countries such as the UK and Germany are actively investigating blockchain solutions for IP management.
- Asia: South Korea and Japan are making significant investments in blockchain applications within creative sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology represents a transformative shift for the intellectual property (IP) industry, addressing longstanding issues such as counterfeiting, piracy, and the complex nature of licensing and royalties. By introducing transparency, security, and automation, blockchain-powered IP marketplaces provide a decentralized alternative that enhances the management, protection, and monetization of IP assets. Features like smart contracts, tokenization, and NFTs offer creators new ways to secure their rights, verify ownership, and generate revenue from their work. As blockchain adoption spreads globally, its role in IP management will expand, driving innovation, boosting efficiency, and creating a fairer ecosystem for creators and stakeholders worldwide. This shift marks the beginning of a new era where managing intellectual property becomes more trustworthy and seamless, propelling the digital economy forward.
FAQs
How would the intellectual rights of the blockchain be classified?
Intellectual rights related to blockchain can primarily be classified into copyrights and patents. Copyrights protect original works of authorship, such as software code and digital content created on blockchain platforms. This grants creators exclusive rights to their work. Patents may apply to novel technological innovations within the blockchain space, such as unique algorithms or processes, preventing others from using or selling these inventions without permission. Additionally, trademarks can protect branding associated with blockchain projects.
Is an NFT intellectual property?
An NFT (Non-Fungible Token) itself is not intellectual property; rather, it serves as a digital certificate of ownership for a unique asset on a blockchain. However, the content linked to an NFT, like digital art or music, can be subject to intellectual property rights, including copyrights or trademarks. The transfer of these rights when an NFT is sold depends on the terms set by the creator at the time of sale.
What is the difference between tokenization and NFT?
Tokenization is the process of converting rights to an asset into a digital token on a blockchain, which can apply to various assets like real estate or stocks. These tokens can be fungible, like cryptocurrencies, or non-fungible, like NFTs. In contrast, NFTs are a specific type of token that represents a unique asset, making them non-fungible. While all NFTs are tokens, not all tokens are NFTs, as tokenization encompasses a broader range of applications.
What are the IP laws in the metaverse?
Intellectual property (IP) laws in the metaverse are evolving alongside this new concept that blends virtual environments with real-world interactions. Copyright protects content created in the metaverse, such as digital art and virtual environments. Trademarks can protect brand identities, including logos and brand names, within the metaverse. Users often need to understand licensing agreements associated with virtual goods to know how their items can be used. Furthermore, the global nature of the metaverse poses jurisdictional challenges, as different regions may have varying laws governing IP rights.


