
Did you happen to know? The average data breach cost was $4.88 million in 2024, the highest average on record. Cyber threats like malware, phishing, and ransomware are growing increasingly sophisticated, prompting organizations to seek advanced solutions. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are technologies that redefine cybersecurity by detecting and responding to threats with unparalleled speed and accuracy.
Cybersecurity confronts numerous challenges as cybercriminals continually adapt their tactics. Traditional methods struggle to keep pace, emphasizing the urgent need for innovative technologies to learn and evolve in real-time. This article delves into the powerful combination of AI and blockchain, exploring their roles in addressing modern cyber threats.
Blockchain: The Future of Cybersecurity
Originally designed to support cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer for cybersecurity. Its decentralized architecture and immutable ledger offer a fresh approach to safeguarding data, making it an essential tool for combating modern cyber threats.
Data Integrity: A Fortress of Immutability
- Permanent, Tamper-Proof Records: Data becomes unchangeable without network consensus once entered into a blockchain. This ensures a rock-solid data integrity guarantee, offering a tamper-resistant record that protects against malicious alterations.
- Immediate Detection of Breaches: Blockchain’s design inherently alerts the network to any attempt to manipulate data, flagging discrepancies and making it nearly impossible for cyber criminals to go undetected.
Trust Through Decentralization and Transparency
- Distributed Networks Build Trust: The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates reliance on a single authority, significantly reducing the risk of a single point of failure or centralized attack. This enhances trust between users by ensuring that no single entity can manipulate or censor data.
- Whole Transparency: Every transaction is publicly verifiable, allowing anyone on the network to audit and verify activities. This high level of Transparency bolsters security and accountability.
Advanced Authentication and Access Control
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based smart contracts automatically execute when pre-set conditions are met, significantly reducing human error, fraud, and unauthorized interference in automated processes.
- Robust Digital Identities: Blockchain can secure digital identities, offering a reliable and hack-resistant method of verifying individuals and devices. This is especially critical in mitigating identity theft or fraudulent access.
Built-In Defense Against Cyberattacks
- Decentralized Data Distribution: By distributing data across multiple nodes, blockchain makes it exponentially harder for hackers to compromise sensitive information. A single server breach won’t damage the entire network.
- DDoS Attack Resilience: Blockchain’s decentralized design makes it inherently resistant to Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, a standard tool for cybercriminals targeting centralized servers.
Supply Chain Security at Every Step
- Real-Time Product Tracking: Blockchain can trace the journey of products across the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and eliminating counterfeit goods. This Transparency promotes trust and enhances accountability across industries.
- Immutable Accountability: Every stage of a supply chain transaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating a transparent, tamper-proof ledger that holds all parties accountable.
Key Benefits of AI-Based Cybersecurity on Blockchain
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity market size was evaluated at USD 17.4 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit around USD 102.78 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 19.43% between 2023 and 2032. The fusion of AI and blockchain technology brings powerful improvements to cybersecurity: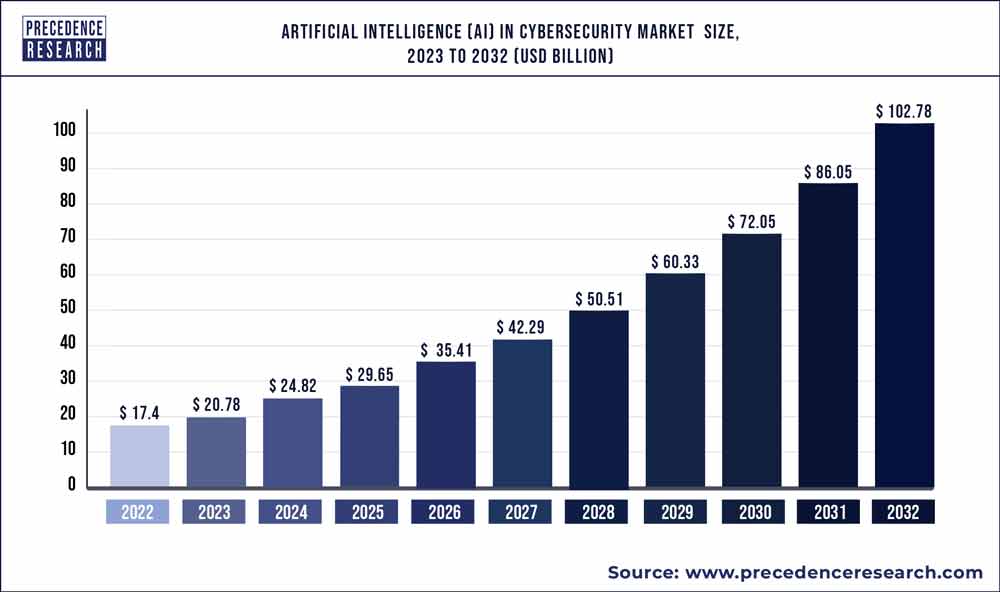
Advanced Threat Detection
- Anomaly Detection: AI analyzes blockchain data to spot irregular patterns, flagging potential security breaches.
- Real-Time Monitoring: AI continuously monitors blockchain networks, detecting threats as they happen.
Stronger Fraud Prevention
- Identity Verification: AI ensures the authenticity of digital identities, reducing fraudulent transactions.
- Fraud Detection: AI analyses transaction behaviour by identifying suspicious activities like money laundering.
Enhanced Privacy Protection
- Privacy Solutions: AI creates privacy-preserving techniques that protect data while allowing valuable analysis.
- Data Governance: AI enforces ethical use of data on blockchain, ensuring compliance with governance policies.
Boosted Efficiency and Automation
- Task Automation: AI automates routine security tasks, streamlining processes like traffic monitoring and signature verification.
- Resource Optimization: AI intelligently allocates resources to focus on critical security areas.
Smart Contract Security
- Vulnerability Detection: AI identifies flaws in smart contracts to prevent potential attacks.
- Automated Auditing: AI audits smart contracts automatically, ensuring they function as intended.
Scalability Enhancements
- Consensus Optimization: AI improves blockchain scalability by optimizing consensus algorithms.
- Sharding Implementation: AI supports sharding techniques to divide the blockchain, boosting performance.
Decentralized Security Architecture: A Paradigm Shift in Cybersecurity
Decentralized security architecture marks a transformative change from traditional centralized security models. Instead of relying on a single authority to control security, decentralized systems distribute responsibilities across various nodes or entities in a network, fundamentally transforming security management.
Key Features of Decentralized Security Architecture
- Distributed Trust lies at the heart of decentralized security. Unlike centralized systems, where trust is placed in a single entity, decentralized networks distribute trust among multiple nodes. This dramatically reduces the risk of a single point of failure and makes it far more challenging for attackers to breach the system.
- Resilience is another significant advantage of decentralization. Even if one node is compromised, the rest of the system remains operational, making it much harder for attackers to cause widespread damage. The distributed nature of these systems ensures that they can withstand targeted attacks with minimal disruption.
- Autonomy plays a crucial role in the security of decentralized networks. Each node operates independently, and attackers are unlikely to gain control over the entire network by compromising a single point. This autonomy adds another layer of security, making the system harder to manipulate.
- Lastly, Transparency is a defining trait of decentralized systems. Since transactions and data are publicly visible, it becomes much easier to detect suspicious activity, ensuring that malicious behaviour is identified and dealt with swiftly.
Real-World Applications of Decentralized Security
- Blockchain technology is the most well-known example of decentralized security. Blockchain operates on a distributed ledger, where transactions are immutable and nearly impossible to alter without widespread consensus. This makes blockchain highly secure and resistant to tampering.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks are another example. By distributing data and resources across multiple nodes, P2P networks ensure that no single point of failure exists, making them more robust against attacks.
- Distributed storage systems, such as the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), take decentralization a step further by spreading data across a network of nodes. This approach enhances resilience against censorship and minimizes the risk of data loss.
Key AI-Based Cybersecurity Protocols on Blockchain
AI and blockchain technology fusion revolutionises cybersecurity by introducing cutting-edge protocols that strengthen network security, enhance privacy, and optimize performance.
-
Anomaly Detection
AI excels in real-time monitoring by continuously scanning blockchain networks for unusual activities or patterns that could signal a security breach. Through pattern recognition, AI can sift through enormous amounts of data, identifying subtle anomalies that human analysts might easily miss. Furthermore, AI-powered predictive analytics use historical data and current trends to forecast potential threats, allowing organizations to take proactive steps before issues escalate.
-
Smart Contract Security
AI is critical in securing smart contracts by conducting automatic vulnerability assessments. It identifies weaknesses such as reentrancy attacks or integer overflows that could be exploited. In addition, AI enables automated auditing of smart contracts, ensuring continuous adherence to security best practices. With predictive maintenance, AI can foresee potential issues within smart contracts and recommend timely updates, preventing vulnerabilities from being exploited.
-
Identity Verification and Authentication
AI enhances identity verification by utilizing biometric verification methods, such as facial recognition or fingerprint analysis, to confirm the authenticity of digital identities. Additionally, through behavioural analysis, AI can monitor user behaviour patterns, flagging anomalies that suggest unauthorized access or fraudulent activity.
-
DDoS Attack Mitigation
AI is instrumental in defending against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks by performing deep traffic analysis. It can recognize and mitigate malicious traffic patterns before they overwhelm the network. Through adaptive routing, AI dynamically adjusts routing protocols to avoid compromised nodes and distribute traffic evenly, ensuring the network remains operational during an attack.
-
Privacy-Preserving Techniques
AI integrates advanced homomorphic encryption techniques, allowing computations on encrypted data without revealing sensitive information. This ensures data privacy while still enabling valuable operations. Additionally, AI leverages differential privacy, a method that adds noise to data sets, protecting individual privacy while maintaining the overall integrity of the analysis.
Future Trends in AI and Blockchain for Cybersecurity
The convergence of AI and blockchain is set to transform cybersecurity by enabling advanced threat detection, privacy protection, and automated incident response. AI will enhance real-time anomaly detection and predictive threat intelligence and automate cyberattack responses, while blockchain-based identity management will give users more control over their data. As quantum computing progresses, quantum-resistant cryptography and quantum AI will emerge to safeguard systems. Ethical considerations and global governance will become vital, especially as these technologies secure IoT devices and supply chains. AI and blockchain will shape a more secure and resilient digital future.
Conclusion
The integration of AI and blockchain is reshaping the future of cybersecurity by providing robust, scalable, and intelligent defence mechanisms. From AI-powered threat detection and smart contract auditing to blockchain’s decentralized architecture and tamper-proof records, these technologies offer unparalleled protection against cyberattacks. As AI evolves and blockchain adoption grows, this dynamic duo will play a pivotal role in safeguarding digital infrastructures across industries, ensuring a more secure and resilient future.
FAQS
Is AI used in airport security?
AI is used in airport security to enhance screening processes, analyze passenger behaviour, and detect potential threats. AI-powered systems can scan luggage more accurately, identify suspicious items, and use facial recognition for faster, more secure passenger identification.
How can generative AI be used in cybersecurity?
Generative AI can help cybersecurity by simulating potential attack scenarios, creating realistic threat models, and generating test cases to identify vulnerabilities. It can also be used to develop more sophisticated phishing detection and adaptive defence systems.
How is AI used in security systems?
AI enhances security systems by automating surveillance, analyzing real-time data, and identifying suspicious behaviour or anomalies. It can also integrate with biometric authentication, improving access control and threat detection.
How is AI used in threat detection?
AI in threat detection analyzes network traffic, user behaviour, and system logs to identify unusual activities that could indicate a cyberattack. It employs machine learning models to predict potential threats and quickly respond to evolving attack patterns.
How do security cameras use AI?
AI in security cameras enables intelligent video analytics, allowing the system to detect specific activities like motion, loitering, or unauthorized access. AI can also recognize faces, objects, and behaviours, enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of surveillance systems.


