The rapid evolution of technology has transformed nearly every facet of society, and the world of politics is no exception. Traditional voting systems, plagued by inefficiencies, security breaches, and manual errors, no longer seem sufficient to uphold the democratic principles they protect. This situation has led to a demand for modern, secure, and reliable alternatives that leverage cutting-edge technologies. Enter blockchain and AI-powered voting systems — technologies that promise to reshape the very foundations of voting, making it more transparent, secure, and accessible.
In this article, we will learn how Blockchain voting, paired with artificial intelligence (AI), presents an opportunity to revolutionize elections, bringing much-needed improvements in trust, speed, and scalability. With a focus on decentralized networks and advanced data analytics, these systems could be the key to overcoming the current challenges faced by electoral systems worldwide.
Blockchain and AI-Powered Voting Systems
“Blockchain and AI-powered voting systems” refers to an innovative approach to managing elections. It ensures the transparency and immutability of election data by storing votes in secure, decentralized ledgers. Simultaneously, AI enhances the voting process by improving voter accessibility, fraud detection, and election management through advanced algorithms and data analysis.At their core, these systems integrate the best of both technologies. Blockchain’s decentralized nature guarantees that no single entity can manipulate election results, while AI automates complex tasks, helping to ensure that elections run smoothly and fairly.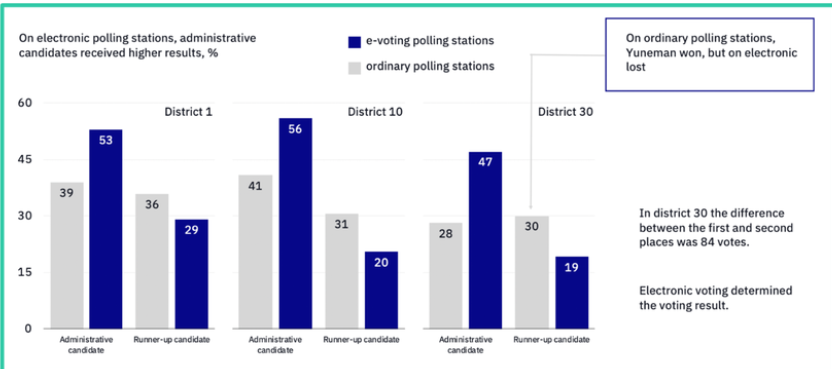
The Importance of Election Security
In recent years, election security has become a growing concern, with allegations of voter fraud, external interference, and data manipulation making headlines worldwide. Whether paper-based or electronic, traditional voting systems have shown themselves to be vulnerable to manipulation, whether through hacking, vote tampering, or ballot destruction.In this climate, blockchain and AI-powered voting systems provide a much-needed solution. By creating a transparent, immutable ledger for votes and incorporating AI’s powerful analytics tools, these systems can dramatically reduce the likelihood of fraud and provide greater confidence in the election results.
How Blockchain Can Transform Voting
Blockchain technology, known for its robust security and transparency, presents an innovative approach to modernizing the voting process. Here’s a straightforward explanation of how it operates: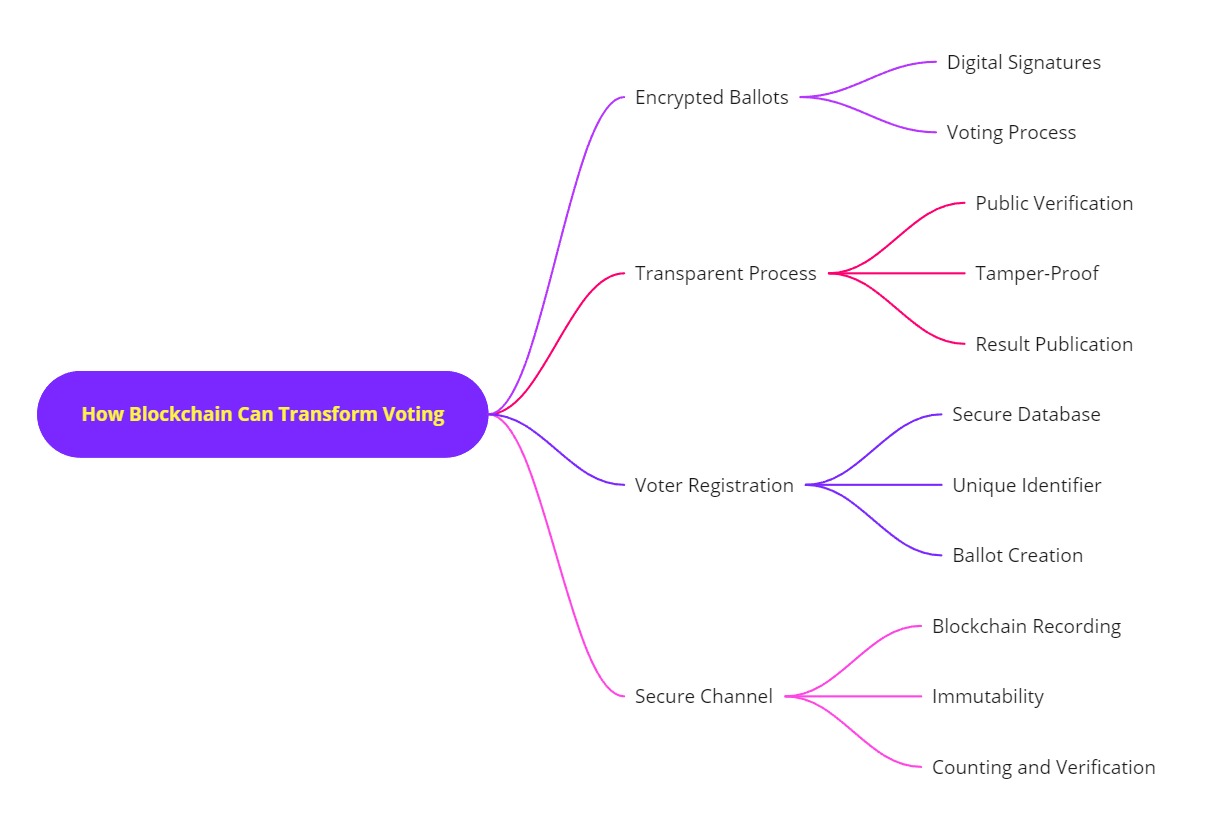 Voter Registration
Voter Registration
- Secure Database: Voter information is maintained within a secure blockchain network.
- Unique Identifier: Each voter is assigned a distinct cryptographic key, ensuring individual identification and preventing duplicate voting.
Ballot Creation
- Encrypted Ballots: Ballots are generated and encrypted using advanced cryptographic methods.
- Digital Signatures: Each ballot includes a digital signature from the voter, confirming its validity and origin.
Voting Process
- Secure Channel: Voters can cast their ballots through a secure online or offline method.
- Blockchain Recording: The encrypted ballot is logged on the blockchain as a transaction.
- Immutability: Once a ballot is recorded, it cannot be altered, safeguarding it from tampering.
Counting and Verification
- Transparent Process: The counting is conducted by multiple nodes within the blockchain network.
- Public Verification: The voting results can be verified by anyone through the blockchain, promoting transparency and trust.
- Tamper-Proof: The immutable blockchain design makes it nearly impossible to manipulate the outcome.
Result Publication
- Decentralized Verification: Final results are established through consensus among network nodes.
- Public Access: Results are made publicly accessible, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Critical Advantages of Blockchain Voting
Enhanced Security: The decentralized architecture makes hacking or manipulation exceedingly tricky.Increased Transparency: A public ledger allows anyone to audit the voting process and outcomes.Improved Accessibility: Blockchain can facilitate remote voting, encouraging greater participation.Reduced Fraud: The unchangeable nature of the blockchain prevents issues like double voting and other fraudulent activities.While blockchain shows excellent promise for refining the voting system, challenges remain regarding voter privacy and access for individuals who need internet connectivity. As technology progresses, blockchain could significantly enhance electoral processes’ security, transparency, and efficiency.
AI’s Role in Enhancing Voting Systems
While blockchain secures the voting process, AI enhances it by providing sophisticated tools for data analysis, fraud detection, and efficiency improvements. AI can automate voter registration processes, detect patterns of suspicious activity during voting, and even improve voter engagement by personalizing voting interfaces.In particular, AI excels in the following areas:
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can spot unusual patterns, such as sudden spikes in voter registration in a given area or abnormal voting behaviors, which could indicate electoral fraud.
- Voter Accessibility: AI can provide language translations, adapt interfaces for disabled voters, and even use predictive analytics to forecast turnout, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
- Decision-Making: Machine learning models can predict how different electoral processes or voting systems might impact election outcomes, helping to inform electoral reforms.
How Blockchain Addresses Security Concerns
Blockchain’s decentralized nature provides unparalleled security for voting systems. By recording votes on an immutable ledger, blockchain ensures that no one can change or delete votes once they are cast. Moreover, blockchain-based voting systems can issue unique cryptographic keys to voters, ensuring that only authorized individuals can vote and that each vote is stored securely across the network.Another critical aspect is that voters can verify their vote anytime, creating transparency that traditional voting systems cannot offer.
AI’s Contribution to Election Integrity
AI contributes to election security by identifying irregularities and preventing fraud. By analyzing voting data in real-time, AI can spot unusual activity that might indicate voter suppression or tampering. For instance, AI can detect if many votes are cast simultaneously from the same location, which might indicate an attempt to manipulate the election.AI can also provide predictive analytics that help election organizers prepare for different turnout scenarios. This ensures that resources are employed efficiently to avoid long lines or voter disenfranchisement.
Enhancing Voter Accessibility with AI: Tailoring Voting Experiences
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can improve voter accessibility by customizing the voting experience for diverse populations. Here are some key ways AI can make a difference:
Personalized Voter Information
- Language Translation: AI can convert voter information and instructions into various languages, ensuring individuals with limited English proficiency fully understand the voting process.
- Accessibility Features: AI can generate content in accessible formats, such as Braille or audio descriptions, for voters with disabilities.
Intelligent Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
- 24/7 Assistance: AI-driven chatbots can provide real-time help, answering questions about registration, polling locations, and ballot details at any time.
- Personalized Recommendations: These chatbots can suggest information tailored to each voter’s location and preferences, such as local candidates or specific ballot measures.
Simplifying Voter Registration
- Automated Data Collection: AI can streamline the collection of voter registration data, easing the process for voters and election officials.
- Eligibility Verification: AI can facilitate real-time verification of voter eligibility, ensuring that only qualified individuals can register.
Optimizing Polling Places
- Location Analysis: AI can assess demographic data to determine optimal polling locations, ensuring convenient access for all voters.
- Identifying Accessibility Features: AI can highlight polling places with necessary accessibility features like ramps, elevators, and assistive technologies.
Personalized Ballot Design
- Adaptive Interfaces: AI can design ballots that adapt to meet the specific needs of different voters, such as those with visual impairments or cognitive challenges.
- Multilingual Options: Ballots can be available in multiple languages, ensuring all voters comprehend their choices.
Voter Education
- Tailored Content Delivery: AI can provide personalized educational materials based on individual interests and knowledge levels, enhancing voter understanding.
- Interactive Learning Tools: AI-driven platforms can create engaging learning experiences, making it easier for voters to grasp complex issues and candidates.
Economic Impact of Blockchain and AI on Voting
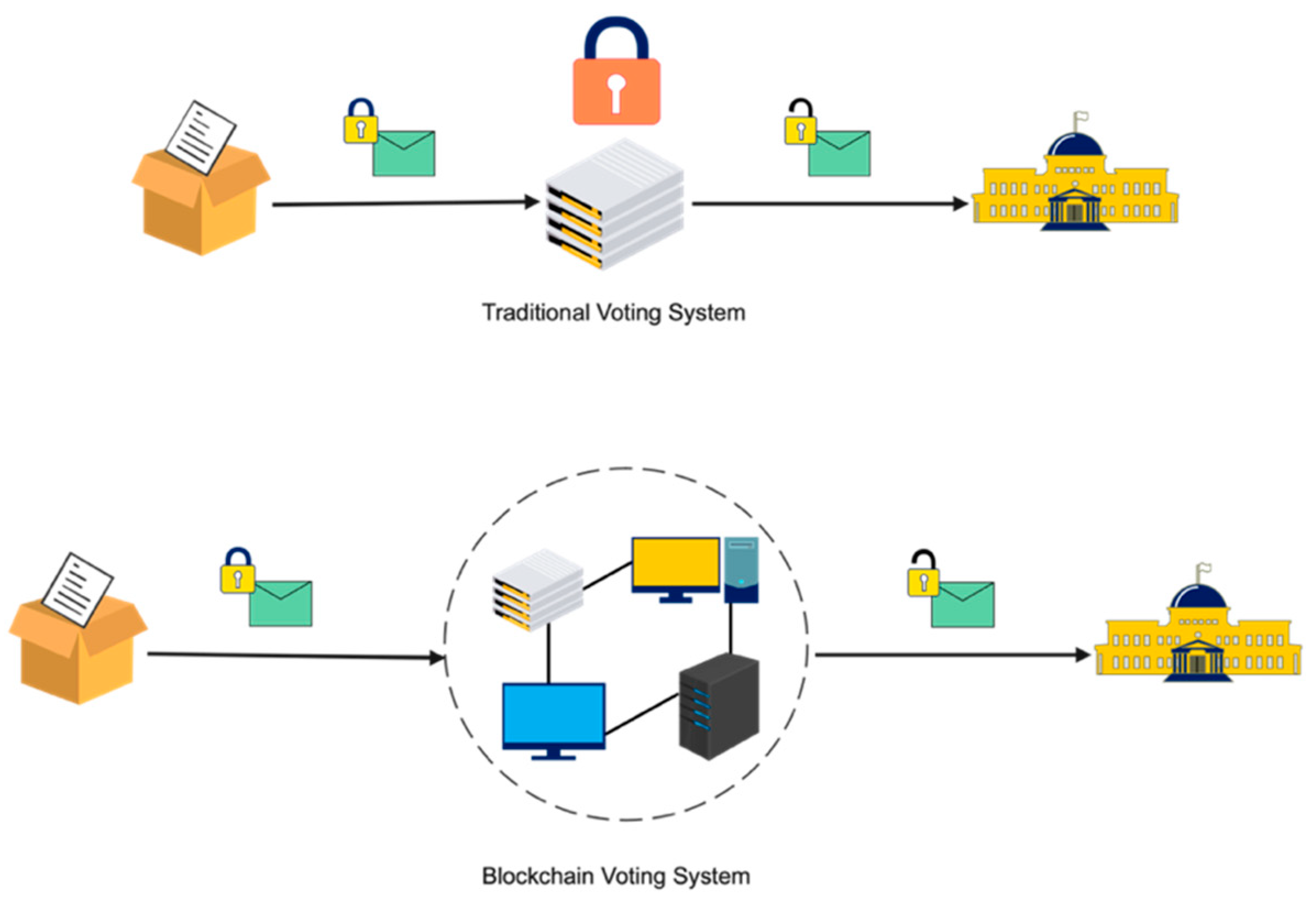
Blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) offer cost-effective solutions to enhance the efficiency and transparency of voting systems, leading to significant economic benefits. By enabling remote voting and automated counting, blockchain reduces the infrastructure costs associated with traditional methods. AI can automate labour-intensive tasks, lowering personnel expenses and preventing fraud, which minimizes costs related to investigations and legal challenges. These technologies also boost voter turnout by simplifying the voting process and improving accessibility. Additionally, blockchain ensures accurate vote counting and transparency, reducing the need for costly recounts. Overall, AI-powered systems can enhance accessibility for all eligible voters.
The Future of Digital Voting
Digital voting promises to transform the electoral process by enhancing accessibility, security, and efficiency. Here are key trends to watch:Blockchain-Based Voting:
- Enhanced Security: The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain can protect against tampering and fraud.
- Increased Transparency: A public ledger allows voters to verify the integrity of the voting process.
Biometric Authentication:
- Improved Security: Fingerprint or facial recognition offers a secure, personalized voting experience.
- Enhanced Accessibility: This technology benefits individuals with disabilities or mobility challenges.
AI-Powered Voter Assistance:
- Customised Information: AI can tailor recommendations to help voters navigate complex issues and candidates.
- Accessibility Features: AI can create inclusive voting systems for those with visual or hearing impairments.
Remote Voting:
- Greater Accessibility: Remote options allow those unable to visit polling places to participate.
- Security Challenges: Ensuring the integrity of remote voting systems will be vital to prevent fraud.
Hybrid Voting Systems:
- Flexibility: Combining in-person and digital options accommodates diverse voter preferences.
- Accessibility: Hybrid systems support participation from individuals with disabilities.
Conclusion
The integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) in voting systems has the potential to revolutionize the electoral process by enhancing security, transparency, and accessibility. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature can protect against tampering and fraud, while AI improves voter engagement through personalized assistance and fraud detection.These technologies promise to make elections more efficient and inclusive, enabling remote and hybrid voting options that broaden participation. However, addressing challenges like privacy concerns and the digital divide is essential to ensure a fair and trustworthy system. Ultimately, the future of voting lies in harnessing these innovations to create a more transparent and participatory democracy.
FAQs
What are the potential privacy concerns associated with using blockchain and AI in voting systems?
Data privacy: The collection and storage of voter data can raise privacy concerns. Data security: Protecting voter data from unauthorized access or breaches is critical.
How can we ensure blockchain and AI-powered voting systems are accessible to all voters?
Accessibility features: Designing systems that are usable by people with disabilities. Education and training: Providing information and support to voters unfamiliar with new technologies.
What are the potential risks of relying too heavily on technology in the electoral process?
Technical failures: The risk of system failures or outages. Digital divide: The potential for excluding voters who do not have access to technology. Loss of trust: If technology is not used effectively or transparently, it can erode public confidence in the electoral process. make it unique and free of plagiarism.


