As the global population migrates toward urban areas, cities must evolve to accommodate the increasing demand for resources and infrastructure. Enter the concept of “smart cities“—metropolitan areas that leverage cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Blockchain to optimize city management, improve the quality of life, and enhance environmental sustainability. But how exactly are AI and Blockchain transforming the smart city landscape?
This article explores various applications of these two technologies and their combined potential to create safer, more efficient, and more sustainable urban environments.
AI for Smart Cities: Transformative Applications in Urban Environments
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the development of smart cities, significantly enhancing urban efficiency, sustainability, and residents’ quality of life. The global Smart Cities Market size was valued at USD 549.1 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.2% from 2023 to 2028. The revenue forecast for 2028 is projected to reach $1,114.4 billion. The base year for estimation is 2022, and the historical data spans from 2023 to 2028. Below are some pivotal applications of AI that are shaping modern urban landscapes: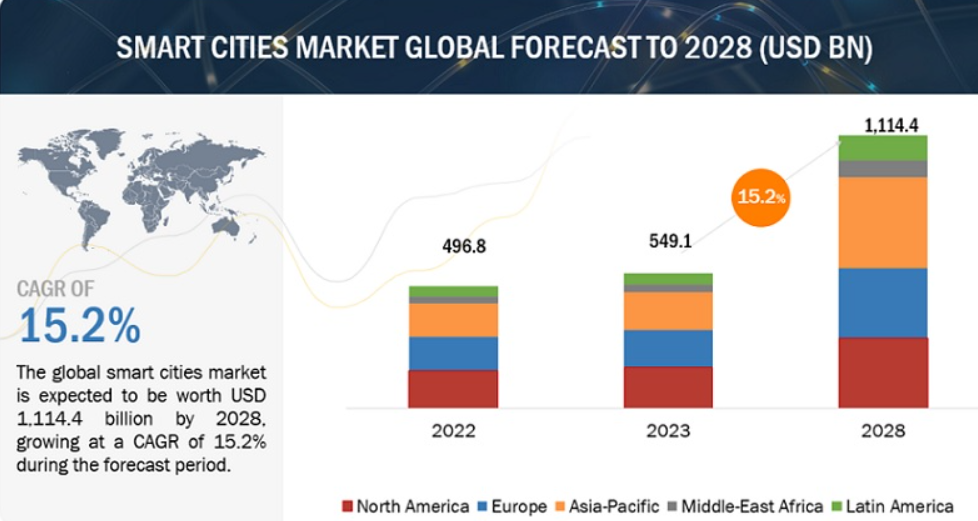
Transportation
- Traffic Management: AI-driven systems analyze real-time traffic data to optimize flow, mitigate congestion, and enhance travel times.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The advancement of self-driving technology aims to reduce accidents, improve traffic efficiency, and alleviate roadway congestion.
- Public Transportation Optimization: AI can enhance public transport systems by optimizing routes, schedules, and resource allocations, ensuring better service delivery.
Energy Management
- Predictive Energy Consumption: AI forecasts energy consumption patterns by examining historical usage data, enabling optimized energy usage across the grid.
- Smart Grids: AI enhances smart grid functionality, allowing for more efficient energy distribution, minimizing losses, and boosting reliability.
- Renewable Energy Integration: AI is crucial in seamlessly including renewable sources, such as solar and wind energy, into existing power systems.
Public Safety and Security
- Video Surveillance Analytics: AI systems can analyze video feeds in real time to detect unusual behaviour, identify potential threats, and assist in crime prevention.
- Emergency Response Optimization: AI can enhance emergency response strategies by evaluating traffic conditions, incident locations, and available resources for quicker deployment.
- Predictive Policing: By analyzing crime data, AI helps identify high-risk areas and predict potential incidents, enabling law enforcement to adopt proactive measures.
Urban Planning and Development
- Urban Data Analytics: AI processes large datasets to uncover trends, patterns, and challenges, aiding informed urban development strategies.
- Smart Infrastructure Design: AI optimizes the planning and maintenance of urban infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings, enhancing their efficiency and longevity.
- Scenario Simulation for Planning: AI enables planners to simulate various scenarios, helping create resilient and sustainable urban environments.
Citizen Services and Engagement
- Personalized Public Services: AI customizes services to meet individual resident needs, significantly improving satisfaction and engagement.
- Efficient Governance: By streamlining administrative processes, AI enhances government efficiency and transparency, fostering greater trust.
- Citizen Participation Platforms: AI supports interactive online platforms that facilitate meaningful citizen engagement and feedback in governance.
AI in Smart Waste Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) revolutionises waste management, helping cities optimize operations and promote sustainability.
- Predictive Waste Collection: AI forecasts waste accumulation to optimize collection routes, reducing trips and fuel use.
- Waste Sorting: AI-powered computer vision accurately classifies waste, improving recycling efficiency.
- Waste Reduction: It identifies practical areas for waste reduction and drives targeted public awareness campaigns.
- Landfill Management: Monitors landfill conditions and predicts waste volumes for improved safety and efficiency.
- Recycling Optimization: AI analyzes market trends for recycled materials, while blockchain ensures transparency in tracking.
Additional Applications
- Healthcare Enhancement: AI improves healthcare delivery by diagnosing diseases and personalizing patient treatment plans.
- Educational Innovations: AI enhances educational experiences through personalized learning pathways and intelligent tutoring systems, improving overall outcomes.
- Environmental Monitoring: AI technologies monitor ecological conditions, detect pollution levels, and promote sustainable practices in urban settings.
The Impact of Blockchain Technology on Smart Cities
Blockchain technology, often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is emerging as a transformative force in various sectors, particularly developing smart cities. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure characteristics provide numerous advantages for enhancing urban infrastructure management.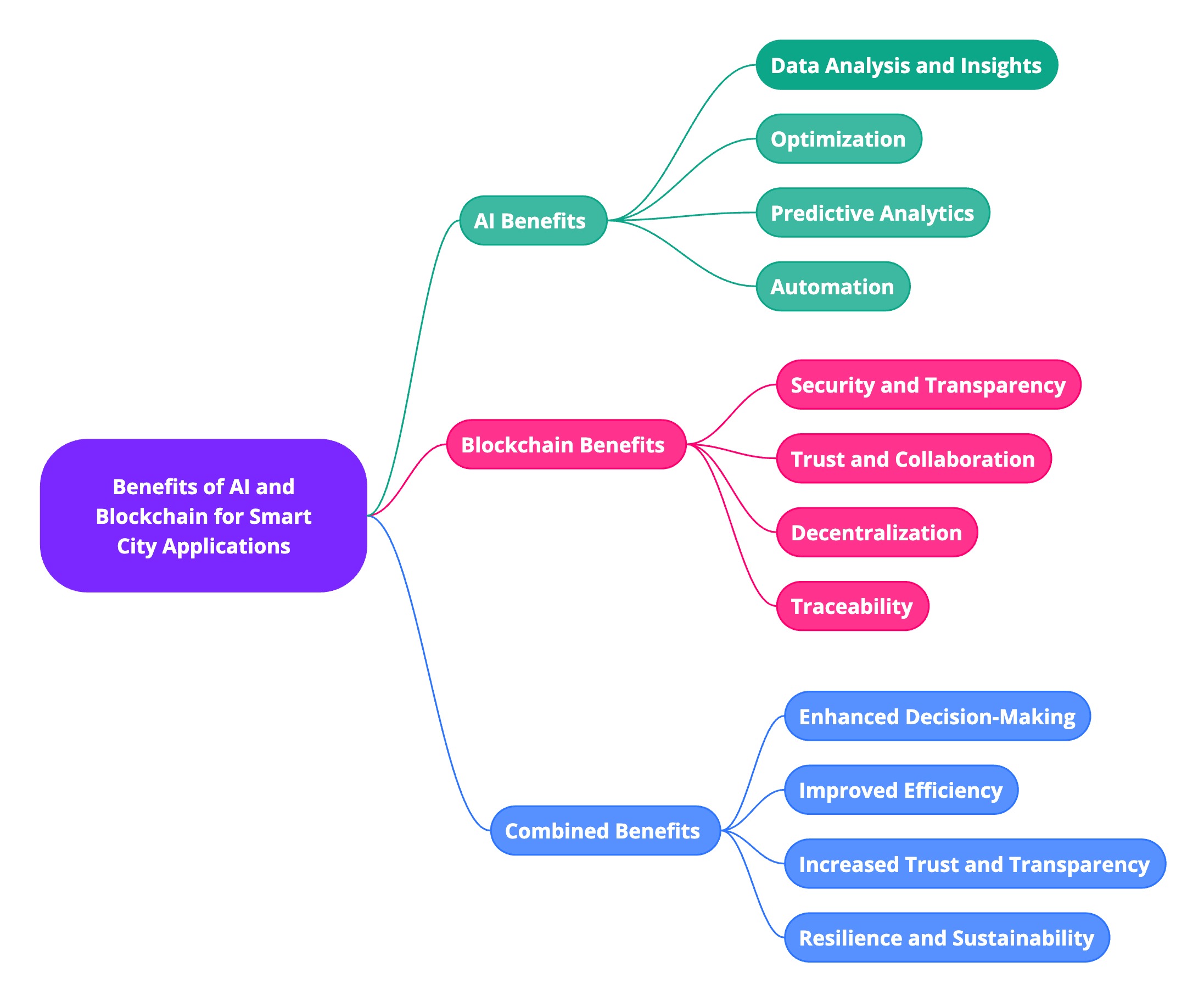
Key Advantages of Blockchain in Smart Cities
Increased Security and Transparency:
- Data Protection: Blockchain guarantees the integrity of information by preventing unauthorized changes and ensuring data is immutable.
- Visibility: Transactions logged on a distributed ledger allow all stakeholders to access and verify information, enhancing transparency.
Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Savings:
- Process Automation: Blockchain technology streamlines operations, minimizing paperwork and reducing errors through automation.
- Cost Efficiency: By removing intermediaries and cutting administrative costs, blockchain contributes significant savings.
Boosted Trust and Collaboration:
- Decentralized Trust: Eliminating a central authority fosters trust among users, promoting cooperation without reliance on a single governing entity.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Blockchain facilitates collaboration among participants, including government bodies, businesses, and citizens.
Strengthened Resilience and Sustainability:
- Infrastructure Resilience: By providing redundancy, blockchain can enhance infrastructure resilience and mitigate risks associated with single points of failure.
- Sustainable Practices: It promotes efficient resource management and waste reduction, supporting the shift toward more sustainable urban practices.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Smart Cities
- Smart Energy Grids: Blockchain enables peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing consumers to sell and purchase excess energy directly from one another.
- Supply Chain Transparency: It tracks the movement of goods, enhancing visibility and reducing the potential for fraud in the supply chain.
- Public Transport Systems: Blockchain can streamline ticketing processes, improve operational efficiency, and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Real Estate Management: The technology simplifies property registration, ownership transfers, and rental agreements through secure, transparent transactions.
- Election Security: Blockchain offers a secure platform for voting, enhancing transparency and citizen participation in democratic processes.
Enhancing Data Privacy in Smart Cities: The Role of Blockchain Technology
As smart cities continue to evolve, ensuring data privacy becomes increasingly critical. Blockchain technology offers innovative solutions to safeguard sensitive information, enhancing trust and security within urban environments. Here are some key applications of blockchain for data privacy in smart cities:
- Identity Management
Blockchain technology can establish secure digital identities, allowing individuals to control their personal information. Using cryptographic techniques, blockchain protects identities from unauthorized access and potential misuse, empowering residents with ownership over their data.
- Secure Data Sharing
Blockchain facilitates secure and controlled data sharing among stakeholders, including government agencies, private enterprises, and citizens. By employing a decentralized ledger, blockchain ensures that data exchanges are transparent, traceable, and resistant to tampering, fostering participant trust.
- Privacy for IoT Data
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices generates vast amounts of data, which can be vulnerable to breaches. Blockchain can enhance the privacy of IoT-generated data by securing its collection, storage, and usage. This decentralized approach ensures that only authorized entities can access sensitive information, mitigating privacy risks.
- Securing Healthcare Information
In healthcare, blockchain can be vital in securing sensitive patient data. By creating an immutable record of medical information, blockchain prevents unauthorized access and ensures that healthcare providers can only view relevant data with the patient’s consent. This level of security not only protects patient privacy but also enhances the integrity of healthcare systems.
Blockchain in Municipal Payments
Blockchain technology enhances municipal payment systems by improving security, efficiency, and transparency.
- Property Tax Payments: Streamlines payments, reducing fraud and increasing efficiency.
- Utility Bill Payments: Facilitates secure transactions for water, electricity, and gas.
- Permit and License Fees: Ensures transparent management, minimizing corruption risks.
- Government Grants and Subsidies: Optimizes distribution, enhancing accountability and reducing fraud.
How AI and Blockchain Improve Citizen Engagement: Participatory Governance and Civic Empowerment
When combined, AI and blockchain can revolutionize citizen engagement and foster participatory governance in smart cities. By leveraging these technologies, cities can create more inclusive, transparent, and responsive urban environments.
AI for Enhanced Citizen Engagement:
- Personalized Communication: AI can analyze citizen data to tailor communication and services, ensuring residents receive relevant and timely information.
- Social Media Monitoring: AI can monitor social media platforms to identify public concerns and sentiments, allowing governments to respond effectively.
- Virtual Town Halls: AI-powered virtual town halls can facilitate more accessible and inclusive public participation, even for those who cannot attend physical meetings.
Blockchain for Trust and Transparency:
- Decentralized Governance: Blockchain can empower citizens by creating decentralized governance platforms where they can participate in decision-making processes.
- Transparent Voting: Blockchain-based voting systems can ensure the integrity and security of elections, increasing citizen trust in the democratic process.
- Data Privacy: Blockchain can protect citizen data by ensuring transparency and accountability in data collection and usage.
Case Studies: AI and Blockchain in Smart Cities
Several cities worldwide are leading the way in integrating AI and blockchain technologies to enhance their operations and services. Here are notable examples:
Dubai, UAE
- Traffic Management:
- Dubai has introduced AI-driven traffic management systems to streamline traffic flow, decrease congestion, and enhance travel times.
- Land Registry on Blockchain:
- The city has implemented a blockchain-based land registry to provide transparency, security, and efficiency in property transactions.
Seoul, South Korea
- Waste Management Optimization:
- Seoul utilizes AI-enabled sensors to optimize waste collection routes, boosting recycling efforts and minimizing waste.
- Voting Security with Blockchain:
- The city has tested blockchain-based voting systems to ensure the integrity and transparency of electoral processes.
Taipei, Taiwan
- Smart Grid Technology:
- Taipei employs an AI-powered smart grid to optimize energy distribution, minimize energy loss, and incorporate renewable energy sources.
- Food Safety via Blockchain:
- The city has adopted blockchain technology to monitor the movement of food products, enhancing safety and transparency in the supply chain.
Conclusion
The potential for AI and blockchain to revolutionize urban living through smart city applications is immense. From improving transportation to securing data privacy, these technologies offer a promising path toward more sustainable, efficient, and inclusive cities. As governments and private sectors continue to explore their integration, the future of urban environments looks increasingly bright.
FAQS
What are the future technologies for smart cities?
Future technologies for smart cities include 5G connectivity, enabling faster data transmission; artificial intelligence (AI) for real-time decision-making; blockchain for secure transactions and data integrity; edge computing for processing data closer to the source; and augmented reality (AR) for enhanced urban planning and citizen engagement.
What is Gen AI in smart cities?
Generative AI (Gen AI) in smart cities uses advanced AI models to generate new data and insights. This technology can create simulations for urban planning, optimize resource allocation, and enhance predictive analytics for public services, fostering innovation and improved decision-making.
What are the four pillars of a smart city?
The four pillars of a smart city are smart governance, which focuses on efficient and transparent administration; smart mobility, which enhances transportation systems; smart environment, which promotes sustainability and ecological balance; and smart living, which improves the quality of life through technology-driven services and amenities.
Is a smart city an IoT application?
A smart city is fundamentally an application of the Internet of Things (IoT). It utilizes IoT devices and sensors to collect data, enabling real-time monitoring and management of urban services such as traffic, waste, energy, and public safety. This ultimately enhances the city’s overall efficiency and livability.


